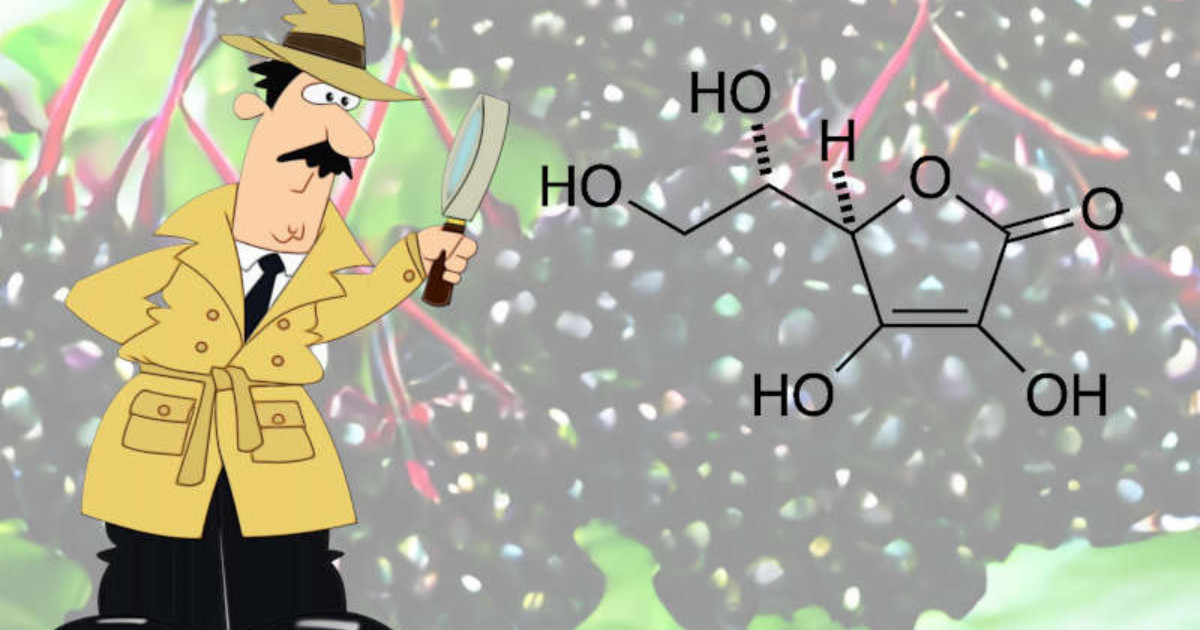
Let’s take a look at the Elderberry vs Vitamin C debate. Some considerations need to be made here to get a better perspective.
Elderberry does contain Vitamin C. Elderberry is also rich in vitamins and minerals such as Vitamins A, B, and E, and minerals like potassium, calcium, and iron. Being high in antioxidants it can also help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Table of Contents
Which is Better Elderberry or Vitamin C?
As we take a closer look at the power of Vitamin C vs Elderberry for immunity, there are some considerations we need to keep in mind.
The body’s ability to store Vitamin C is limited as it is a water-soluble vitamin. What you don’t use or need is flushed out. So bulking up on it might not provide many benefits if your body doesn’t need the extra.
Where it does play some key roles not just in helping the body to fight colds, but, did you know that the body requires Vitamin C to help absorb iron?
Elderberry is a Reliable Source of Vitamin C
The Vitamin C content of elderberries can vary depending on factors such as the type of elderberry, the region where it is grown, and the time of year when it is harvested. However, elderberries are generally considered to be a good source of Vitamin C.
According to the United States Department of Health and Human Services (ODS), 100 grams (g) of raw elderberries contain approximately 35.96 milligrams (mg) of Vitamin C (based on a calculation of 145g of elderberries containing 52.2mg Vitamin C). This is about 60% of the recommended daily intake (RDI) for Vitamin C for adult men and women, which is 60mg per day. 1
Keep in mind that it is not generally considered safe to consume raw elderberries, so they will need to be processed. So what will that do to the Vitamin C content in elderberries? Given the discussion about elderberry vs Vitamin C, this might present a challenge. We’ll get into that soon.
It’s worth noting that the Vitamin C content of elderberries can be affected by factors such as how they are processed and stored. Let’s consider the processing here as elderberries will need to be processed or cooked.
Processing Elderberry vs Vitamin C from Other Sources
So let’s assume that processing consists of cooking. Cooking or drying elderberries in an elevated temperature environment can reduce their Vitamin C content. Similarly, it can be lost during storage, so it’s best to consume elderberries as fresh as possible.
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is sensitive to heat, light, and air. When exposed to these factors, it can break down and become less potent.
The rate at which it is destroyed depends on the temperature and the length of time it is exposed to heat. It is more stable at lower temperatures and is less likely to be destroyed by heat.
However, it can still be lost through a process called “thermal degradation,” which occurs when Vitamin C breaks down due to the heat and moisture that are present during cooking or processing.
When considered in conjunction with the data from the International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research which suggests the percentage of Vitamin C can reduce by between 9.94% and 16.57% in the first 5 minutes, and between 29.94% and 37.43% in the first 15 minutes, and between 49.91% and 64.71% in the first 30 minutes, the cooking time for elderberries will have a material impact on the residual Vitamin C content. 2
The lower (-) and higher (+) ranges of potential loss of Vitamin C based on a crude application of the model from this study suggest that the impact could be as much as between a loss of 9.94% and 64.71% depending on the time frame.
| Sample | Raw | 5 Min | % Loss | 15 Min | % Loss | 30 Min | % Loss |
| Pepper | 61.56 | 54.32 | 11.76 | 39.84 | 35.28 | 21.72 | 64.71 |
| Green Peas | 43.44 | 38.84 | 10.59 | 28.96 | 33.33 | 18.12 | 58.28 |
| Spinach | 36.2 | 32.6 | 9.94 | 25.36 | 29.94 | 14.48 | 60.00 |
| Pumpkin | 28.96 | 25.36 | 12.43 | 18.12 | 37.43 | 10.88 | 62.43 |
| Carrot | 25.36 | 21.72 | 16.57 | 14.48 | 33.33 | 10.88 | 49.91 |
| Elderberry (-) | 35.96 | 32.39 | 9.94 | 25.19 | 29.94 | 18.01 | 49.91 |
| Elderberry (+) | 35.96 | 30.00 | 16.57 | 22.50 | 37.43 | 12.69 | 64.71 |
Elderberry lower (-) and higher (+) ranges of potential loss of Vitamin C
For example, boiling vegetables for long periods or cooking them at high temperatures can cause a significant loss of Vitamin C. Similarly, storing foods in direct sunlight or at high temperatures can also cause it to break down.
Did you know that HerbiTea’s Iron Fluorine Tea contains elderberries?
To preserve the Vitamin C content of foods, it is best to cook them at lower temperatures for shorter periods and to store them in a cool, dry place.
So, how much Vitamin C is retained by elderberries once they are processed?
How does that Stack Up to Oranges?
According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), 100g of raw oranges contain about 26.7mg of Vitamin C. 3
So how do raw oranges (which do not require cooking) stack up against our assessment of cooked elderberries and their reduction in Vitamin C content?
| Sample | Raw | 5 Min | % Diff | 15 Min | % Diff | 30 Min | % Diff |
| Orange | 26.70 | 26.70 | 0 | 26.70 | 0 | 26.70 | 0 |
| Elderberry (-) | 35.96 | 32.39 | 121.31 | 25.19 | 77.77 | 18.01 | 55.60 |
| Elderberry (+) | 35.96 | 30.00 | 112.36 | 22.50 | 75.00 | 12.69 | 42.30 |
Vitamin C content in oranges is fixed in this table as the samples would not require cooking
Elderberry lower (-) and higher (+) ranges of potential loss of Vitamin C
% Diff = parentage difference of orange to elderberry Vitamin C content
Based on a subjective application of this proposed data, the timeframe for cooking elderberries where they are generally considered safe to consume would place them in a depreciated Vitamin C range to the extent that oranges would arguably have a higher nutritional value of Vitamin C.
Many Vitamin C products on the market are in the thousands of milligrams. So these are arguably higher than either elderberries or oranges as two natural sources. However, some argue that the isolation of ascorbic acid in a tablet form does not have the same effect as when sourced directly from foods naturally.
Can you take Elderberry and Vitamin C Together?
Yes, you can take elderberry with Vitamin C. As mentioned earlier, with Vitamin C being water soluble, you can’t overdose on it. What is not needed is flushed out of the system.
There is no evidence to suggest that taking elderberry and Vitamin C together would cause any negative interactions or side effects.
Some people may find that taking elderberry and Vitamin C together can provide additional health benefits, as both nutrients are thought to support immune function and overall wellness.

The 4 Big Elderberry vs Vitamin C Questions Answered
Is Elderberry the same as Vitamin C?
No. Raw elderberries are a fruit that contains Vitamin C. Vitamin C is not a fruit, it is a vitamin found in the fruit.
Saying Elderberry is the same as Vitamin C is like saying sugar is the same as soda. Soda will typically contain sugar, but it is not sugar by definition.
Should I take Elderberry and Vitamin C?
Can you take vitamin C and elderberry together, or will there be a conflict? Yes, you can take them together, and no, there isn’t likely to be a conflict.
Should you take them, well, that’s a discussion to have with a qualified professional face-to-face who can assess your specific needs.
Does Elderberry have more Vitamin C than Oranges?
This might be the biggest disruptor for some in the elderberry vs Vitamin C debate. Elderberry does not have more Vitamin C than oranges. Oranges are one of the most well-known sources of Vitamin C, and they are generally considered to be a richer source of the vitamin compared to elderberry.
It’s worth noting that the Vitamin C content of both elderberries and oranges can vary depending on factors such as the type of fruit, the region where it is grown, and at what time in the year they are harvested.
As mentioned earlier, oranges have a higher Vitamin C content than elderberries.
In addition, the Vitamin C content of both fruits can be affected by how they are processed and stored, specifically when considering how heat reduces the Vitamin C content over time.
Is it OK to take Elderberry every day?
There is no issue with making elderberries a part of your daily routine as long as they have been suitably processed to remove any toxins. The main consideration here is the level of sambunigrin and how this affects the body.
Consider the potential impacts of having too much exposure to sambunigrin as referenced in Are Elderberries Poisonous? 3 Important Facts.
Conclusion
Addressing the elderberry vs Vitamin C discussion, elderberries may have their Vitamin C content diminished as a part of the processing to make them safe to consume. Oranges, as a source of Vitamin C, require no processing to make them safe to consume, so, their ability to provide the the body with this vitamin in an unadulterated form is naturally higher.
If you were to take supplements, such as Vitamin C tablets, you may find that you are dosing your body with much more than it needs, and essentially flushing out the large part of what you are taking in.
This is not to say that there isn’t a place for products like these. Each person’s needs are dynamic and unique, and there may well be a time and a place to take supplements over seeking the minerals and vitamins from food sources.
Ultimately, seeking professional guidance in a face-to-face format is the optimal means of achieving what is going to work best for you. Anything you can learn about the topic you are seeking support on beforehand will help you frame the advice provided and take action in a manner that you believe is best for you and your needs.
References
- “USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference Release 28” – National Agricultural Library, 28 October 2020 [ODS] [Archive] ↩︎
- “Effect Of Heating On Vitamin C Content Of Some Selected Vegetables” – N.C. Igwemmar, S.A. Kolawole, I.A. Imran, November 2013 [IJSTR] [Archive] ↩︎
- “Tangerines, (mandarin oranges), raw” – US Department of Agriculture, 1 April 2019 [USDA] [Archive] ↩︎
Last Updated on 5 months by D&C Editorial Team